
New study by a team of scientists led by Dr. Gou Huiyang from HPSTAR and Dr. Biao Wan of Zhengzhou University has succeeded in synthesizing a new electride BaCu with Cu anions, which exhibits some unique properties except for retaining the properties of traditional 2D electrides. The discovery of layered BaCu electride will not only deepen our understanding of electrides, but also facilitate the discovery and potential application of novel 2D electrides with transition metal anions. The study is published in JACS.
Electrides are a unique class of ionic compounds, in which the electrons act as anions. The electron anions give electrides a variety of attractive physical properties such as significant quantum effects, and high carrier mobility etc. which make electrides have potential applications in energy storage and electronic devices. Two-dimensional(2D) electrides with loosely bound nature and negligible mass of anionic electrons exhibit superior physical properties. However, due to the complex formation conditions, the currently known 2D electrides are limited to specific structural prototypes and components.
The team synthesized a distinct 2D electride of BaCu with Cu anions confined to the interlayer spaces of the BaCu frameworks. Although BaCu is composed of metallic elements, it exhibits typical 2D material characteristics and extremely low exfoliation energy. Adjacent Cu ions form a planar cellular network through the hybridizations of s-d orbitals. The theoretical calculations and XANES measurements reveal that Cu ions are in a negative valence state, and near the Fermi level, the interaction between the Cu atom and the adjacent Ba atom produces significant antibonding properties, thereby increasing the energy of the valence electrons, allowing them to escape from the atomic orbitals and form electron anions between the layers. Room-temperature resistivity measurement shows that BaCu has high electrical conductivity, similar to the typical 2D electride Ca2N.
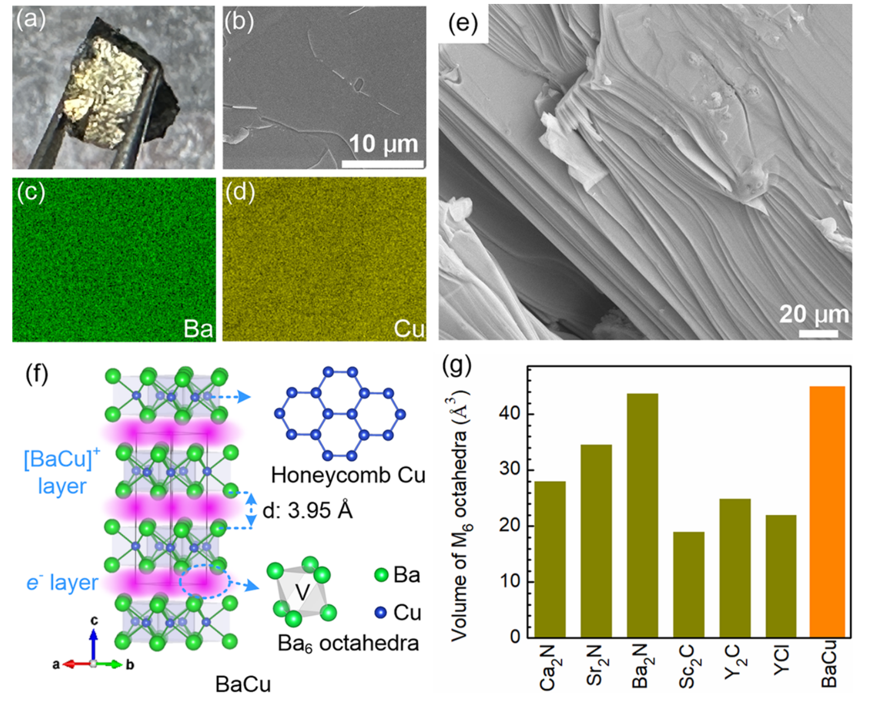
Caption: Synthesis of BaCu. Synthesized BaCu sample (a). FESEM (b, e) and elemental-mapping analysis (c, d) of BaCu. Crystal structure of BaCu from single-crystal analysis, where V represents the voids in the center of the Ba6 octahedra (f). The volume of Ba6 octahedra in the BaCu interlayer spaces compared to typical 2D electrides (g).
"Compared to typical 2D electrides, the electron anions in BaCu show discrete distribution and apparent orbital hybridizations with the surrounding atoms,” said Dr. Gou.“This unique interaction gives BaCu an unusual low work function. The orbital hybridization of electron anions also brings unique isotropic physical properties to BaCu and theoretical studies further predict the possibility of exfoliation of monolayer BaCu which has semimetallic characteristics.”